Table of contents
What is GPT?
GPT(Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) is an AI model developed by OpenAI that uses NLP for human-like conversations. It's based on the GPT-3 model trained on a massive amount of text data to generate contextually relevant responses. Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence models that can generate new content, such as text, images, or audio, that is similar to content it has been trained on. ChatGPT is an example of a generative AI model that has been specifically designed for human-like conversations.
How ChatGPT works?
Fundamentally GPT-3 (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) takes in input text (tokens) and outputs some amount of text (tokens). One of the key features of ChatGPT is its ability to generate responses that are contextually relevant to the conversation. This is achieved through the use of a technique called text completion, which involves predicting the next word or phrase in a sentence based on the text that precedes it. This allows ChatGPT to generate responses that are not only grammatically correct but also contextually relevant.
ChatGPT is trained on a massive corpus of data that includes everything from news articles to social media posts. This allows it to understand a wide range of topics and generate responses that are relevant to the conversation at hand. Additionally, ChatGPT can be fine-tuned to specific use cases, such as customer service or technical support, to generate responses that are tailored to the needs of the user.
Note: 1 token doesn’t equal 1 word, this is due to white space, punctuation and the splitting of longer words. As a simple estimate, 1000 tokens is equal to about 750 words.
Training vs Inference
Due to the model's size and the time it takes for the model to learn the parameter values, training the model is extremely expensive. However, running the trained model during inference is much cheaper since you don't need to update weights, but instead, convert input text to vectors and perform matrix operations. In short, training the model is much more expensive as compared to running the trained model.
Words to Vectors
We can’t calculate an error loss between two words, but we can calculate the difference between two vectors. Text is converted to tokens and then the tokens are encoded as vectors. An embedding neural network is used to convert the tokens into a vector, GPT-3 initially used a 12,288 dimension vector. Each piece of text can then be represented as tokens, which can be converted to vectors.
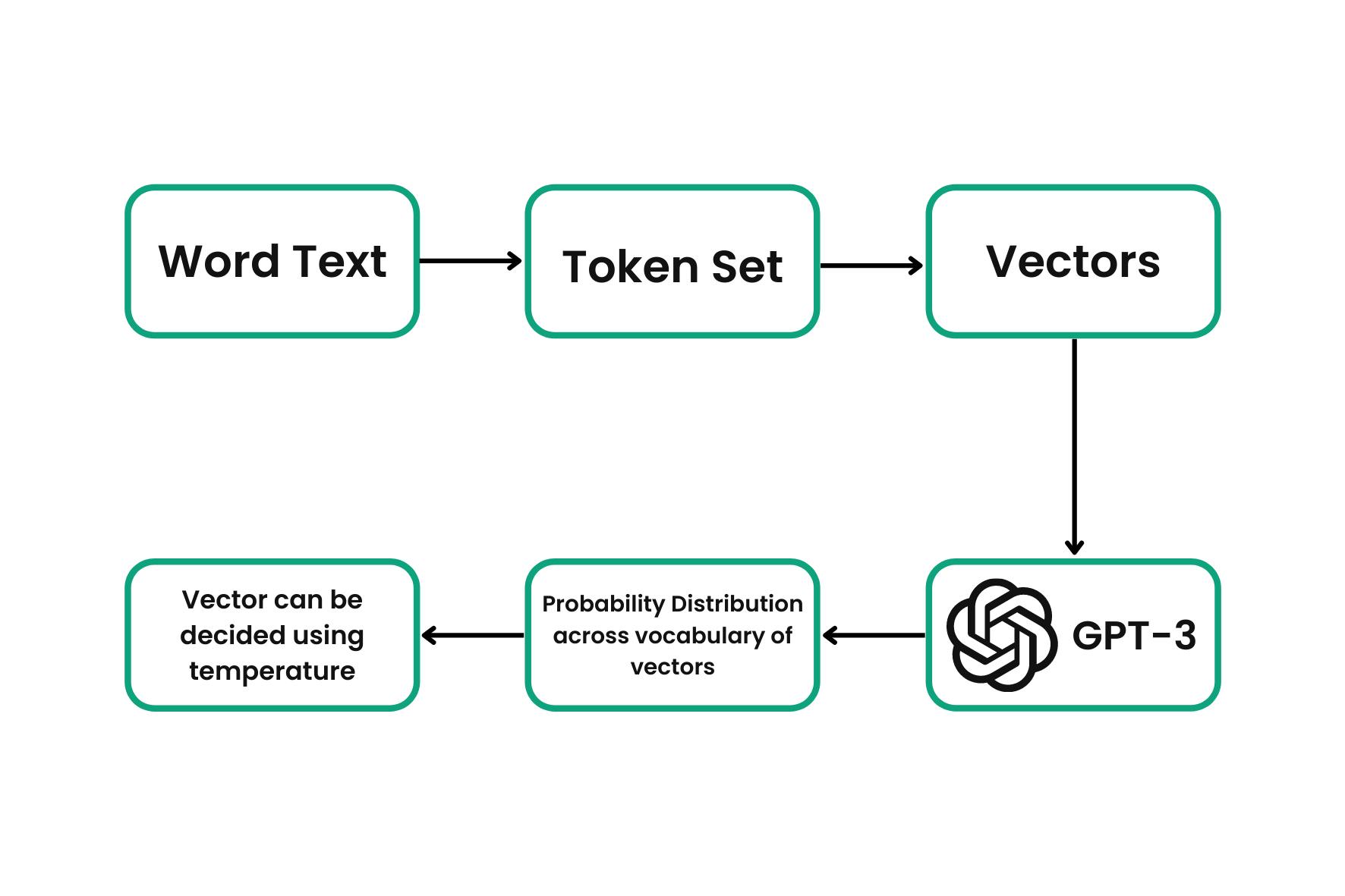
Word text is converted to a token set. Tokens are converted to vectors. Vectors are passed into GPT-3 and the model returns a probability distribution across the vocabulary of vectors. We can then specify via “temperature” which vector should appear next (which can then be reversed back into text).
That's all for now, thank you for reading. Let's connect and follow for more such content.